What is Agentic RAG? A Complete Guide for December 2025

Many AI agents don't remember previous conversations, requiring users to as the same questions and provide the same background information each session. While standard RAG pulls information from documents, agentic RAG systems come in to bridge the gap between static retrieval and truly intelligent, memory-powered AI interactions. But even agentic RAG has limitations: it's complex, expensive and still prone to losing context. That's where a persistent memory layer can improve the agent operation. Rather than RAG, this layer can not only deliver better context persistence but also improve token efficiency.
TLDR:
Traditional RAG retrieves documents per query, stateless and limited in personalization.
Agentic RAG adds autonomous agents that plan, reason, and adapt, improving handling of complex queries.
Both approaches still struggle with long-term context and can be costly and complex.
A persistent memory layer like Mem0 gives true session-to-session recall, reducing token use and improving accuracy compared with RAG alone.
What is Agentic RAG?
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems work like a basic search engine: you ask a question, they find relevant documents, and generate an answer. That's it. No memory, no learning, no adaptation. This technology has been integrated with AI agents to create Agentic RAG. Instead of simple query-response cycles, these systems use intelligent agents that can plan, reason, and make decisions about how to retrieve and use information. Think of it as giving your RAG system a brain that can think several steps ahead.
The key difference lies in autonomy and adaptability. While traditional RAG follows a fixed pipeline (retrieve → rank → generate), agentic RAG uses agents that can:
Analyze complex queries and break them into sub-tasks
Choose different retrieval strategies based on context
Learn from previous interactions to improve future responses
Coordinate multiple information sources dynamically
Agentic RAG represents the evolution from static information retrieval to intelligent, adaptive knowledge systems that can reason about what information to retrieve and how to use it effectively.
Understanding RAG vs Agentic RAG
Let's break down the fundamental differences between traditional RAG and agentic RAG systems.
Traditional RAG operates like a well-organized library with a helpful librarian. You ask a question, the system searches through documents, finds relevant passages, and generates an answer based on that information. The process is linear, predictable, and stateless.
Component | Traditional RAG | Agentic RAG |
|---|---|---|
Query Processing | Single-step retrieval | Multi-step reasoning and planning |
Decision Making | Fixed pipeline | Adaptive strategy selection |
Memory | Stateless sessions | Persistent context and learning |
Adaptability | Static responses | Evolving based on interactions |
Complexity Handling | Simple queries only | Complex, multi-part questions |
Instead of a simple librarian, imagine having a research team that can strategize, delegate tasks, and learn from experience. The core advancement lies in the agent's ability to plan and reason. When you ask a complex question, an agentic RAG system might:
Break your query into multiple sub-questions
Determine which information sources are most relevant
Decide on the optimal retrieval strategy
Synthesize information from multiple sources
Remember the context for future interactions
But an agentic RAG system without memory, while performing admirable during any given individual session, ultimately fails because it is stateless: it loses valuable context that could improve future responses.
Consider a practical example. If you ask a traditional RAG system "What's the best approach for my project?", it might give generic advice. An agentic RAG system with memory would remember your previous discussions about project constraints, team size, budget, and preferences, providing truly personalized recommendations.
However, even agentic RAG systems remain fundamentally stateless across sessions, limiting their ability to build long-term context or personalization.
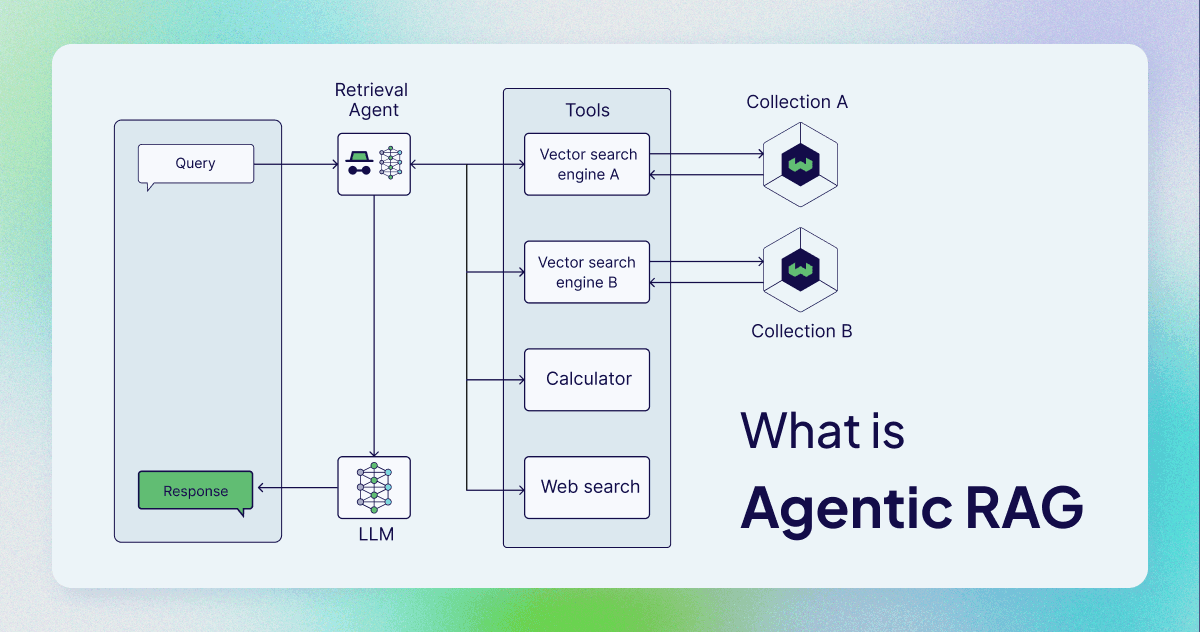
Core Components of Agentic RAG Architecture
Let's look at the key components that make these systems work.
Routing Agents serve as the traffic controllers of agentic RAG systems. They analyze incoming queries and determine the best path for information retrieval. Unlike traditional RAG systems that follow a single pipeline, routing agents can direct queries to specialized retrievers, different knowledge bases, or even external APIs based on the query's nature and context.
Query Planning Agents break down complex questions into manageable sub-tasks. When you ask "How can I improve my customer retention while reducing costs?", a query planning agent might decompose this into separate searches for retention strategies, cost reduction methods, and industry-specific best practices.
ReAct Agents (Reasoning and Acting) are the most sophisticated component. These agents can reason about information, take actions based on their analysis, and iterate on their approach. They embody the "think before you act" principle, making agentic RAG systems far more intelligent than traditional approaches.
The architecture can scale from single-agent systems to complex multi-agent orchestrations:
Single-Agent Architecture: One intelligent agent handles all tasks but with enhanced reasoning abilities
Multi-Agent Architecture: Specialized agents work together, each optimized for specific tasks like retrieval, reasoning, or synthesis
Memory infrastructure plays an important role in these architectures. This is where different types of memory become important, working memory for immediate context, episodic memory for past interactions, and semantic memory for learned patterns.
The power of agentic RAG lies in how these agents coordinate and learn from each other to create increasingly intelligent systems.
Real-World Applications and Use Cases
Agentic RAG systems are changing industries by providing intelligent, context-aware information retrieval that adapts to specific business needs and user requirements.
Customer Support Revolution
In customer support, agentic RAG systems go beyond simple FAQ matching. They analyze customer history, understand context from previous interactions, and proactively suggest solutions. Instead of asking customers to repeat their problems, these systems remember past issues and build complete support profiles.
Healthcare and Medical Applications
Healthcare organizations use agentic RAG for clinical decision support, where agents can connect patient history, current symptoms, and medical literature to assist healthcare providers. The systems adapt to different medical specialties and learn from clinical outcomes to improve recommendations over time.
Educational Personalization
Educational technology has seen remarkable success with agentic RAG. RevisionDojo enhanced personalized learning by implementing memory-powered agents that remember student learning patterns, strengths, and areas for improvement. The system adapts content difficulty and teaching approaches based on individual student progress.
Similarly, OpenNote scaled learning while reducing token costs by 40%. Their agentic RAG system remembers how students learn best and adjusts visual presentations accordingly.
Financial Services and Analysis
Financial institutions use agentic RAG for market analysis, risk assessment, and client advisory services. Agents can connect market data, regulatory changes, and client portfolios to provide personalized investment recommendations that evolve with market conditions.
The key advantage across all these applications is the ability to maintain context and learn from interactions. Traditional RAG systems treat each query independently, but agentic RAG builds understanding over time.
According to analysis on agentic RAG, organizations report major improvements in user satisfaction and better performance when implementing these systems.
Enhanced Memory with Mem0
Mem0 turns agentic RAG from simple automation into systems that truly learn and adapt. It’s a universal, self-improving memory layer for LLMs that compresses chat history into optimized representations, cutting token usage and latency while preserving rich context across sessions.
Unlike agentic RAG’s complex agent pipelines, Mem0 provides persistent memory natively, enabling better accuracy, fewer tokens, and deeper personalization without custom history management.
The Memory Advantage
Mem0’s hybrid architecture combines vector search, knowledge graphs, and key-value storage to deliver human-like recall:
Intelligent Context Management: captures key facts, preferences, and moments automatically
Memory Compression: cuts token usage by up to 80% with no loss of context
Adaptive Updates: refines stored knowledge and resolves contradictions over time
Multi-Modal Support: stores both text and visual context for richer agent behaviors
Performance That Matters
The open-source Mem0 repository has over 40,000 stars, reflecting developer trust in its approach.
For startups building memory-powered AI, the Mem0 Startup Program provides six months of free access to Pro features, along with direct support from our team.

Final thoughts on building intelligent RAG systems with memory
The shift from traditional RAG to agentic RAG reflects a move from static retrieval toward systems that can reason and coordinate, but both approaches remain limited by statelessness across sessions. Without a durable way to retain context, even sophisticated agents must repeatedly reconstruct information through retrieval pipelines. Persistent memory addresses this structural gap by separating recall from retrieval, enabling continuity and personalization without replaying full histories or documents on every interaction. For teams building intelligent RAG systems, the key question is not whether memory matters, but how and when to introduce it without adding unnecessary architectural complexity.
FAQs
How do agentic RAG systems coordinate agents?
Router, planner, and reasoning agents to break queries into steps, choose retrievers, and iteratively refine answers.
How does memory architecture impact token cost?
Naive approaches append entire conversation history to every prompt, driving token costs up. Systems with memory compression or structured recall can reduce token usage by 70-90% while improving response quality.
How do you benchmark agentic RAG performance?
Teams typically measure:
Context Recall Accuracy: Did the system retrieve the right facts?
Token Efficiency: How many tokens per answer vs. baseline RAG?
Latency: Time to response when coordinating multiple agents.
User Satisfaction: Qualitative score for relevance and helpfulness.
What's the main difference between traditional RAG and agentic RAG?
Traditional RAG follows a simple retrieve-and-generate pipeline for each query, while agentic RAG uses intelligent agents that can plan, reason, and learn from interactions. Agentic RAG maintains memory across sessions and can break complex queries into sub-tasks, making it far more adaptive and personalized.
Subscribe To New Posts
Subscribe for fresh articles and updates. It’s quick, easy, and free.














