LangGraph Tutorial: How to Build Smarter AI Agents with Memory (December 2025)
Building AI agents that operate reliably in real-world workflows requires more than stateless prompt-response loops. Modern agent systems need the ability to reason over time, revisit decisions, and accumulate context across interactions. LangGraph enables this shift by supporting cyclical, stateful agent workflows where control flow, memory, and decision-making are first-class primitives. This guide explores how LangGraph’s architecture transforms simple chatbots into adaptive agents, and why persistent memory for AI applications is the missing layer that allows these systems to retain context, learn from experience, and improve continuously rather than resetting on every interaction.
TLDR:
LangGraph enables cyclical, decision-driven agent workflows but only maintains state within a single session
Session-scoped state limits personalization since agents forget user preferences once interactions end
Persistent memory extends LangGraph agents across sessions, enabling long-term context and adaptation
Memory layers reduce repeated retrieval and prompt replay, improving accuracy, latency, and user experience
Combining LangGraph with a persistent memory solution turns agents from session-based tools to personalized long-term companions
Adding Mem0 memory achieves 26% higher accuracy with 90% lower latency than baseline approaches
What is LangGraph?
LangGraph is a fundamental shift in how we build AI agents. While traditional chatbots follow linear question-answer patterns, LangGraph creates cyclical workflows where agents can think, act, observe, and decide their next steps dynamically.
Think of LangGraph as the framework that changes your AI from a simple responder into a thoughtful problem-solver. It's part of the LangChain ecosystem but tackles a specific need: building agents that can handle complex, multi-step reasoning tasks that require state management and decision-making features.
The magic happens through three core concepts:
Nodes are individual functions or LLM calls.
Edges define how information flows between nodes.
State management maintains context throughout the entire workflow, allowing agents to remember what they've learned and build upon previous interactions.
LangGraph's cyclical architecture allows agents to iterate on problems, refine their approaches, and make intelligent decisions based on accumulated context instead of starting fresh with each interaction.
LangGraph vs LangChain: When to Use Each
Understanding when to use LangGraph versus LangChain comes down to workflow complexity and state requirements. LangChain excels at linear workflows where you have a clear sequence of steps from input to output.
Feature | LangChain | LangGraph |
|---|---|---|
Workflow Type | Linear chains | Cyclical graphs |
State Management | Limited | Advanced |
Decision Making | Minimal | Sophisticated |
Tool Selection | Predetermined | Adaptive |
Complexity | Simple to moderate | Moderate to complex |
LangChain works perfectly for straightforward tasks like document summarization, simple Q&A systems, or basic RAG implementations. The linear chain approach handles these scenarios efficiently without unnecessary complexity.
LangGraph shines when you need agents that can make decisions, iterate on problems, or handle unpredictable workflows. If your agent needs to select tools, verify outputs, or revisit earlier steps, LangGraph provides a structured way to manage those workflows.
It's important to remember that while there are distinct use cases for LangChain and LangGraph, these tools actually complement each other, not compete with each other. Many production systems use LangChain components within LangGraph workflows, using the strengths of both approaches.
Understanding LangGraph Core Components
The foundation of any LangGraph application rests on three fundamental building blocks that work together to create intelligent agent behavior.
Nodes are the workhorses of your graph. Each node represents a specific function, whether that's calling an LLM, executing a tool, or processing data. Nodes receive the current state, perform their designated task, and return updated state information.
Edges define the flow of control between nodes. Unlike simple sequential chains, LangGraph supports conditional edges that make routing decisions based on the current state. This allows flexible workflows where the agent's next action depends on what it learned from previous steps.
State Management maintains shared context throughout the entire workflow execution. The StateGraph class provides a centralized way to track information, so each node has access to relevant context from previous operations.
Together, these three building blocks let you design workflows where agents can branch, loop, and adapt dynamically based on context. The beauty of the architecture lies in its flexibility. Agents can check their progress at any point, decide whether to continue with the current approach, or pivot to a different strategy entirely.
Example: A Personalized Research Assistant
Imagine building a research assistant (using LangChain and LangGraph) that searches the web, analyzes findings, and remembers that you prefer bullet-point summaries. The agent, then, easily transitions from searching to analyzing to updating memory, adapting its behavior at each step.
The key to making this happen is a stateful agent, like LangGraph. As you probably know, stateless agents fail because they can't remember anything. In a stateful environment like LangGraph, the agent remembers but only within the parameters of the existing session. LangGraph supports long-term state through external persistence and checkpointing, but memory is not a first-class abstraction. Any persistence beyond a single session must be explicitly designed, stored, and retrieved by the developer. As a result, personalization is possible, but only with custom memory logic layered into the graph. Without this additional infrastructure, agents default to session-scoped context and lose learned preferences, such as you preferring bullet-point summaries, once an interaction ends.
To see how this works in practice, including how to persist state and inject long-term memory into a LangGraph workflow, refer to our LangGraph integration documentation. It walks through how memory is stored, retrieved, and made available to agents across sessions without restructuring the core graph.
Improving LangGraph State With Persistent Memory
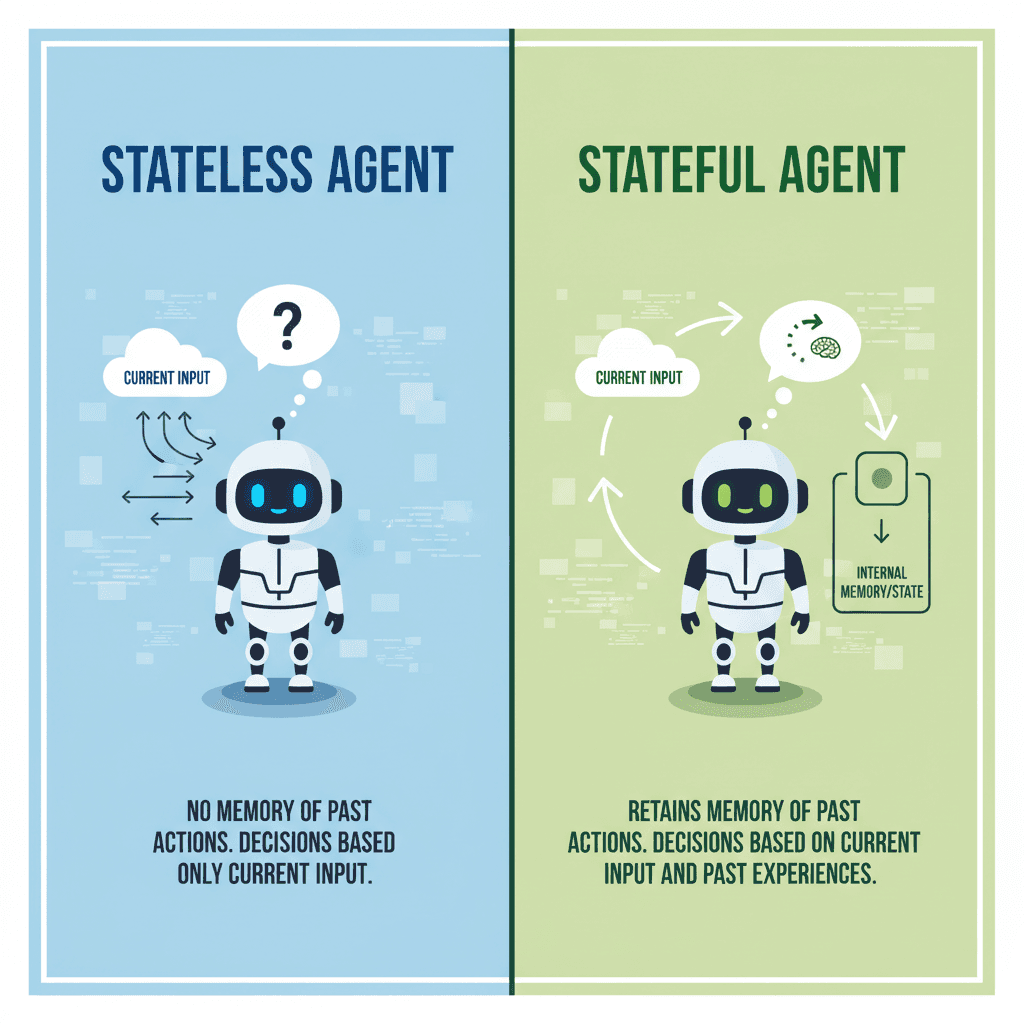
Memory represents the difference between basic automation and truly intelligent assistance. While LangGraph provides excellent state management within individual sessions, persistent memory across sessions changes agent abilities entirely. LangGraph's built-in state management handles immediate context well. The StateGraph maintains information throughout a single workflow execution, letting agents build upon previous steps and make informed decisions. However, session-based state has limitations. When a conversation ends, the context disappears. Users must re-explain their preferences, repeat background information, and start relationship-building from scratch with each new interaction.
By integrating a persistent memory like Mem0 with LangGraph, the change in the agent experience can be remarkable. Instead of treating each interaction as isolated, the agent builds a relationship with you over time. Back to the research assistant example, the agent now remembers that you prefer detailed research with bullet-point formatting, automatically adapting future responses to match your preferences.
In the research agent example, LangGraph can persist state across sessions using threads and checkpointers, but what gets stored and how it’s recalled is entirely up to the developer. Preferences like formatting style must be explicitly written to state, retrieved on future runs, and injected back into the workflow. Without this additional memory logic, agents behave as if preferences are session-bound, requiring users to restate them over time with every new interaction.
Mem0's memory compression tackles these limitations by intelligently storing and retrieving relevant context across sessions. The memory layer can provide a LangGraph agent persistent memory across sessions, letting them build long-term relationships and learn user preferences over time. When your LangGraph agent includes a Mem0 layer, it remembers that you like bullet-point summaries without you having to tell it each time.
Thankfully, integrating a persistent memory layer into your LangGraph agents isn't difficult. Check out this guide to see how memory integration works in practice. But also remember that not all memory layers perform equally. Check out our research on memory system performance and the detailed benchmark comparison to understand the technical advantages of different options.
Tools and External Integrations As Part of Persistent Memory
User preferences, like wanting bullet-point summaries, are not the only thing stored in persistent memory. Real-world agents need access to external tools and services to be truly useful. LangGraph makes tool integration straightforward while maintaining the flexibility to choose tools dynamically based on context. The specific tools that an agent might use (web search, calculators, or APIs) are directly related to the interaction with the user.
Let's take the example of a user asking the research assistant for some facts about a specific topic. So if the user says, "I don't like those results. Let's try a different browser" and then eventually says, "wow, those results are great", the agent can store which tool (i.e., a web browser perhaps) returned the best results. Consider a customer service agent who learns a user prefers detailed technical explanations over simple answers. The memory system stores this preference, and future interactions automatically select tools and approaches that match the user's communication style. In this way, memory systems store tool effectiveness allowing increasingly intelligent tool selection over time. Then, the actual tools to which the agent integrates and uses as part of engaging with the user become part of the persistent knowledge about that user.
Tool integration patterns:
Conditional routing: Choose tools based on query analysis
Sequential execution: Chain tools together for complex tasks
Parallel processing: Run multiple tools simultaneously
Fallback strategies: Handle tool failures gracefully
Implementing Advanced Agent Patterns
Advanced LangGraph patterns unlock sophisticated agent behaviors that can handle complex real-world scenarios with multiple decision points and collaborative workflows.
Multi-agent systems show the most powerful patterns. Instead of building monolithic agents, you create specialized agents that collaborate on complex tasks.
Human-in-the-loop workflows allow agents to escalate complex decisions or seek clarification when needed. This pattern is important for high-stakes applications where human oversight helps maintain quality and safety.
Conditional routing allows agents to make sophisticated decisions about their next actions based on current context, previous results, or user preferences stored in memory.
Take AI Persistent Memory for a Testdrive
If you are developing an AI agent with LangGraph and want to incorporate a persistent memory layer while you are developing, consider checking out the startup program. It provides free access to advanced memory features while you're developing and testing your agent systems.
A Note About Memory Integration
While integrating a memory layer into your LangGraph agent is straightforward, there are some things to keep-in-mind when adding persistence to your agent. Along with normal agent testing, you'll want to make sure that you are debugging the memory layer as well. To tackle that, you should look for a memory layer provider that includes built-in observability. This kind of integrated debugging will provide important insights into memory retrieval, relevance scoring, and how historical context influences agent behavior.
Final thoughts on building advanced AI agents with LangGraph
LangGraph changes how we think about AI agents by allowing cyclical workflows that can adapt and learn from each interaction. The real magic happens when you combine LangGraph's stateful architecture with persistent memory systems like Mem0 that remember user preferences across sessions. Following this LangGraph approach, you can build agents that evolve from simple chatbots into intelligent companions.
FAQ
How do I add persistent memory to my LangGraph agent?
You can integrate a memory layer like Mem0 into your LangGraph workflow by adding memory storage and retrieval nodes to your graph. The memory system stores user preferences and context across sessions, so your agent remembers information beyond individual conversations without requiring users to repeat themselves.
What's the main difference between LangGraph and LangChain?
LangChain handles linear workflows with predetermined steps, while LangGraph creates cyclical workflows where agents can make decisions, loop back to previous steps, and adapt their approach based on context. Use LangChain for simple Q&A or document summarization, and LangGraph when your agent needs to make complex decisions or iterate on problems.
When should I consider adding memory to my AI agent?
If your users need to repeat preferences or background information in each session, or if your agent would benefit from learning user patterns over time, you need persistent memory. Memory integration is particularly valuable for customer service agents, educational tutors, and research assistants that interact with the same users repeatedly.
Can LangGraph agents work together on complex tasks?
Yes, you can build multi-agent systems where specialized agents collaborate and share memory. Each agent handles specific tasks while accessing shared context, so they build upon each other's knowledge rather than starting from scratch. This pattern works well for complex workflows that require different expertise areas.
How much does memory integration improve agent performance?
Memory systems like Mem0 achieve 26% higher response accuracy with 90% lower latency compared to baseline approaches. Beyond performance metrics, memory changes the user experience by eliminating repetitive explanations and allowing agents to adapt to individual preferences automatically.
Subscribe To New Posts
Subscribe for fresh articles and updates. It’s quick, easy, and free.














