Building Enterprise Knowledge Graphs with MCP (December 2025 Update)

Model Context Protocol (MCP) is an open standard, open-source framework introduced by Anthropic in 2024. It allows developers to build secure, two-way connections between their data sources and AI-powered tools. For teams dealing with the difficulty of balancing personalized AI experiences and manageable costs, MCP is a welcome solution, allowing standardized connections between AI systems and persistent memory layers.
TLDR:
MCP standardizes AI–data integration, eliminating custom point-to-point connectors by providing a universal, bidirectional client-server protocol that simplifies connecting AI systems to databases, APIs, file systems, and real-time data sources.
Knowledge graph memory is a natural fit for MCP, enabling AI systems to store and reason over explicit entity relationships (not just vector embeddings), which improves long-term context, cross-conversation understanding, and enterprise knowledge continuity.
Enterprise knowledge graphs introduce scale and governance challenges, requiring robust ontology management, entity resolution, access controls, auditability, and multi-hop relationship queries that traditional databases and vector stores struggle to support.
Production MCP implementations require careful architecture and security, including incremental graph updates, persistent storage, conflict resolution, fine-grained authorization, and adherence to updated MCP security specifications for authentication and token protection.
Successful enterprise adoption depends on phased implementation, starting with high-value use cases, piloting with MCP-compatible graph memory servers, scaling with governance frameworks, and treating knowledge graphs as augmentation layers rather than system replacements.
What Is MCP?
Think of MCP as a universal connector that lets AI models plug into different databases, APIs, and applications in a consistent way.
MCP eliminates the need for custom integrations by providing a single protocol that works across different AI systems and data sources.
Before MCP, connecting AI applications to enterprise data required building custom integrations for each combination of AI tool and data source. This meant that developers spent more time on plumbing than on building intelligent features.
MCP solves this problem by providing a standardized communication layer. Instead of building dozens of point-to-point connections, you implement MCP once and gain access to any MCP-compatible AI system or data source.
The protocol works through a client-server architecture where AI applications act as MCP clients, and data sources expose themselves as MCP servers. This design allows bidirectional communication, letting AI systems both read from and write to connected resources.
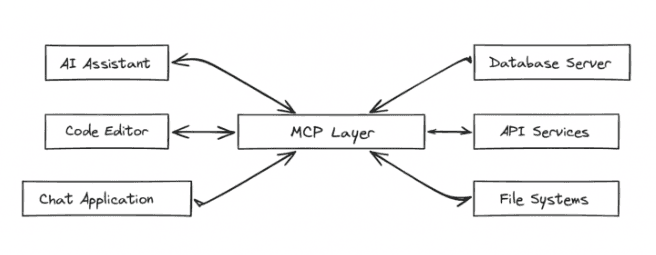
For enterprise knowledge management, MCP solves a key challenge: data silos. The protocol supports multiple resource types including databases, file systems, APIs, and even real-time data streams. This flexibility makes it particularly valuable for building complete knowledge graphs that need to include structured and unstructured data from multiple enterprise systems.
MCP for Knowledge Graph Memory
Because MCP standardizes how AI systems exchange context with data stores, it’s a natural foundation for persistent, relationship-aware memory systems like knowledge graphs. MCP changes AI memory from simple text storage into intelligent, interconnected knowledge systems. Traditional AI memory relies on vector databases that treat each piece of information as isolated embeddings. Knowledge graph memory servers change this by maintaining explicit relationships between entities, creating a web of connected understanding.
When an AI system mentions "John works at Microsoft," a knowledge graph memory server stores this information differently. It creates entities for "John" and "Microsoft" with a "works at" relationship connecting them. Future conversations can use these connections to provide richer context.
Knowledge graph memory lets AI systems understand what happened and how different pieces of information relate to each other across time and conversations.
The knowledge graph memory server implements MCP to expose graph operations as standardized resources, allowing AI clients to query relationships, traverse connections, and update the knowledge structure through consistent MCP calls.

This approach solves a fundamental limitation of vector-only memory systems. While embeddings excel at semantic similarity, they struggle with explicit relationships. A user might mention their spouse in one conversation and their job in another. Vector memory treats these as separate, unrelated facts.
Graph memory connects these dots. When the AI later needs context about the user's family situation and career, it can traverse the relationship graph to understand how these elements interconnect.
The Memento MCP server showcases practical implementation, allowing persistent memory that grows smarter with each interaction while maintaining the standardized MCP interface.
Enterprise Knowledge Graph Fundamentals
Enterprise knowledge graphs differ fundamentally from consumer applications in their complexity, scale, and governance requirements. While a personal knowledge graph might track your preferences and relationships, an enterprise knowledge graph must model complex business processes, regulatory compliance, and thousands of interconnected stakeholders.
The core challenge lies in representing business reality accurately. A customer is more than a name and email contact info: they're connected to contracts, support tickets, purchase history, and organizational hierarchies. Products link to suppliers, manufacturing processes, quality metrics, and market segments.
Enterprise knowledge graphs serve as the connective tissue between disparate data systems, changing isolated information into meaningful business intelligence.
Scale becomes critical when dealing with millions of entities and billions of relationships. A Fortune 500 company might have 100,000 employees, each connected to projects, departments, skills, and external partners. Traditional databases struggle with these multi-hop queries that knowledge graphs handle naturally.
Governance adds another layer of complexity. Enterprise knowledge graphs must enforce access controls, maintain data lineage, and support audit trails. When the AI system retrieves information about a confidential project, it needs to verify permissions across multiple relationship paths.
The enterprise knowledge graph architecture typically includes ontology management, entity resolution, and continuous data synchronization from source systems. This foundation allows AI agents to understand individual facts and the broader business context that makes those facts meaningful.
Building Knowledge Graphs with MCP
Building production-ready knowledge graphs with MCP requires careful attention to entity extraction, relationship modeling, and data persistence. The Memento MCP server provides a solid foundation, but enterprise implementations need additional considerations for scale and reliability.
Entity extraction forms the backbone of any knowledge graph system. Your MCP server must identify meaningful entities from unstructured text and determine when multiple references point to the same real-world object. This entity resolution challenge becomes important when dealing with variations like "John Smith," "J. Smith," and "John from accounting."
The @modelcontextprotocol/server-memory package shows basic memory operations, but enterprise knowledge graphs require more sophisticated relationship modeling. Instead of simple key-value storage, you need to capture complex business relationships with attributes, timestamps, and confidence scores.
Effective knowledge graph construction balances automatic extraction with human oversight, making sure accuracy is maintained while keeping the speed needed for real-time AI interactions.
Your MCP implementation should support incremental updates rather than rebuilding the entire graph with each interaction. When a user mentions a project update, the system should modify existing relationships rather than creating duplicate entities, which requires careful conflict resolution and versioning strategies.
Technical architecture matters for production deployment. Your MCP server needs persistent storage, backup strategies, and monitoring features. Consider implementing graph databases like Neo4j or specialized triple stores that can handle the query patterns your AI memory system will generate.
MCP Security and Governance
Enterprise MCP deployments face security challenges that require complete governance frameworks.
The June 2025 MCP specification updates tackle these concerns by formalizing server authentication roles and mandating token protection through resource indicators. These updates prevent malicious servers from obtaining unauthorized access tokens and create clearer boundaries between client and server responsibilities.
Enterprise knowledge graph implementations must treat MCP security as a foundational requirement, not an afterthought, given the sensitive business data these systems typically access.
Authentication becomes complex when knowledge graphs span multiple enterprise systems. Your MCP servers need to authenticate with AI clients, and also with backend databases, APIs, and document repositories. Implementing proper credential rotation and least-privilege access controls prevents security breaches from cascading across connected systems.
Authorization requires fine-grained control over graph traversal paths. A user might have access to project information but not salary data, even when these entities are connected in the knowledge graph. MCP best practices recommend implementing authorization checks at both the resource and relationship levels.
Data governance policies must cover how long memories persist, who can access relationship data, and how to handle deletion requests.
Regular security audits of your MCP server implementations help identify potential vulnerabilities before they become exploitable attack vectors.
Enterprise Implementation Strategies
Successful enterprise knowledge graph deployments require phased approaches that balance technical complexity with organizational change management. Most implementations fail not due to technical limitations, but because they attempt to solve too many problems simultaneously without setting up clear success criteria.
The discovery phase focuses on identifying high-value use cases where knowledge graphs provide measurable business impact. Rather than trying to model your entire organization, start with specific domains like customer support or product development where relationship data directly improves outcomes.
Implementation Phase | Key Activities | Timeline | Success Metrics |
|---|---|---|---|
Discovery | Data mapping, stakeholder alignment | 2-4 weeks | Use case validation |
Pilot | Graph construction, MCP integration | 6-8 weeks | Query performance |
Scale | Production deployment, governance | 3-6 months | User adoption |
Optimization | Performance tuning, expansion | Ongoing | ROI measurement |
Data integration patterns determine long-term success. Enterprise knowledge graph architectures typically implement federated approaches where MCP servers connect to existing systems without requiring massive data migrations.
The most successful enterprise implementations treat knowledge graphs as augmentation layers rather than replacement systems, preserving existing workflows while adding intelligent connections.
Change management becomes important when AI agents start surfacing insights that cross traditional departmental boundaries. Your AI memory system might reveal connections between sales patterns and support issues that challenge existing organizational assumptions.
Technical governance frameworks should create clear ownership for entity definitions, relationship schemas, and data quality standards. Superblocks' enterprise approach shows how to balance centralized standards with departmental autonomy, allowing new ideas while maintaining consistency across the organization.
Mem0's Knowledge Graph Integration
Several vendors are beginning to implement these principles. With tools like Mem0’s knowledge graph MCP integration, you can now build enterprise-grade memory systems that actually understand relationships between entities instead of just storing isolated facts. By linking data scattered across databases, document repositories, and CRM systems, Mem0’s AI memory creates a single source of truth that connects knowledge across your organization. Our advanced compliance and audit features also provide full visibility into how your data flows through AI interactions, so you can meet regulatory requirements while maintaining intelligent memory functions.
FAQ
How do I integrate MCP with my existing enterprise knowledge systems?
Start with a pilot implementation using the Memento MCP server to connect one high-value data source, then gradually expand to additional systems using the standardized MCP protocol. Most enterprises can complete initial integration in 6-8 weeks by focusing on specific use cases like customer support or product development.
What's the main difference between knowledge graph memory and traditional vector databases?
Knowledge graph memory maintains explicit relationships between entities (like "John works at Microsoft"), while vector databases treat information as isolated embeddings. This relationship modeling allows AI systems to understand connections across conversations and provide better contextual responses.
When should I consider implementing graph memory over simple vector storage?
Consider graph memory when your AI applications need to understand relationships between entities, track evolving user preferences, or connect information across multiple conversations and data sources. It's particularly valuable for enterprise applications where business relationships and hierarchies matter.
Why does MCP security matter for enterprise knowledge graph deployments?
Many MCP servers contain security vulnerabilities including command injection flaws, and enterprise knowledge graphs typically access sensitive business data across multiple systems. Proper authentication, authorization controls, and regular security audits prevent breaches from cascading across connected enterprise systems.
Can I use Mem0's graph memory with my current AI infrastructure?
Yes, Mem0's hybrid architecture integrates with popular AI frameworks like OpenAI APIs, LangChain, and Claude through standardized SDKs, requiring minimal changes to existing systems while adding persistent, relationship-aware memory features.
Final Thoughts on Enterprise Knowledge Graphs with MCP
The shift from isolated AI memory to interconnected knowledge systems represents a fundamental change in how we build intelligent applications. Mem0's approach combines the relationship modeling your enterprise needs with the performance AI systems demand. Your success depends on starting with a focus, prioritizing security from day one, and letting your enterprise knowledge graph evolve naturally.
Subscribe To New Posts
Subscribe for fresh articles and updates. It’s quick, easy, and free.














