The OpenAI Agents SDK Review and Alternatives: Best AI Agent Framework (December 2025)

If you’ve been looking into agent frameworks, you’ve likely come across the OpenAI Agents SDK along with several alternatives. Choosing the wrong one can add unnecessary cost and complexity to your project. To make the process easier, we’ve compared the leading frameworks and outlined where each one performs best.
We’ll also cover how to extend the SDK with a dedicated memory layer, such as Mem0, to overcome its limitations and enable agents that can learn and adapt over time.
TLDR:
Unlike alternatives that are more complex, Agents SDK offers a very simple setup.
Built-in tracing reduces debugging time compared with custom agent systems.
You pay only for model API calls: Agents SDK itself is free and open-source.
The OpenAI Agents SDK is a better choice for rapid development; LangGraph, for complex workflows requiring deep customization.
OpenAI Agents SDK Overview
Agents SDK was launched in March 2025 as a production-ready evolution of OpenAI's experimental Swarm project. Unlike heavyweight alternatives, Agents SDK takes a minimalist approach with just four core primitives that handle the key building blocks of agent systems.

The framework's lightweight architecture makes it immediately accessible to developers familiar with OpenAI's ecosystem. You get Agents equipped with instructions and tools, Handoffs for delegation between agents, and Guardrails for input/output validation.
What sets Agents SDK apart is its provider-agnostic design. While optimized for OpenAI models, it works with more than 100 other LLMs, through the Chat Completions API. This flexibility prevents vendor lock-in while maintaining the simplicity that makes rapid development possible.
The GitHub repository shows active development with regular updates that handle real-world production needs.
Core Features and Functions
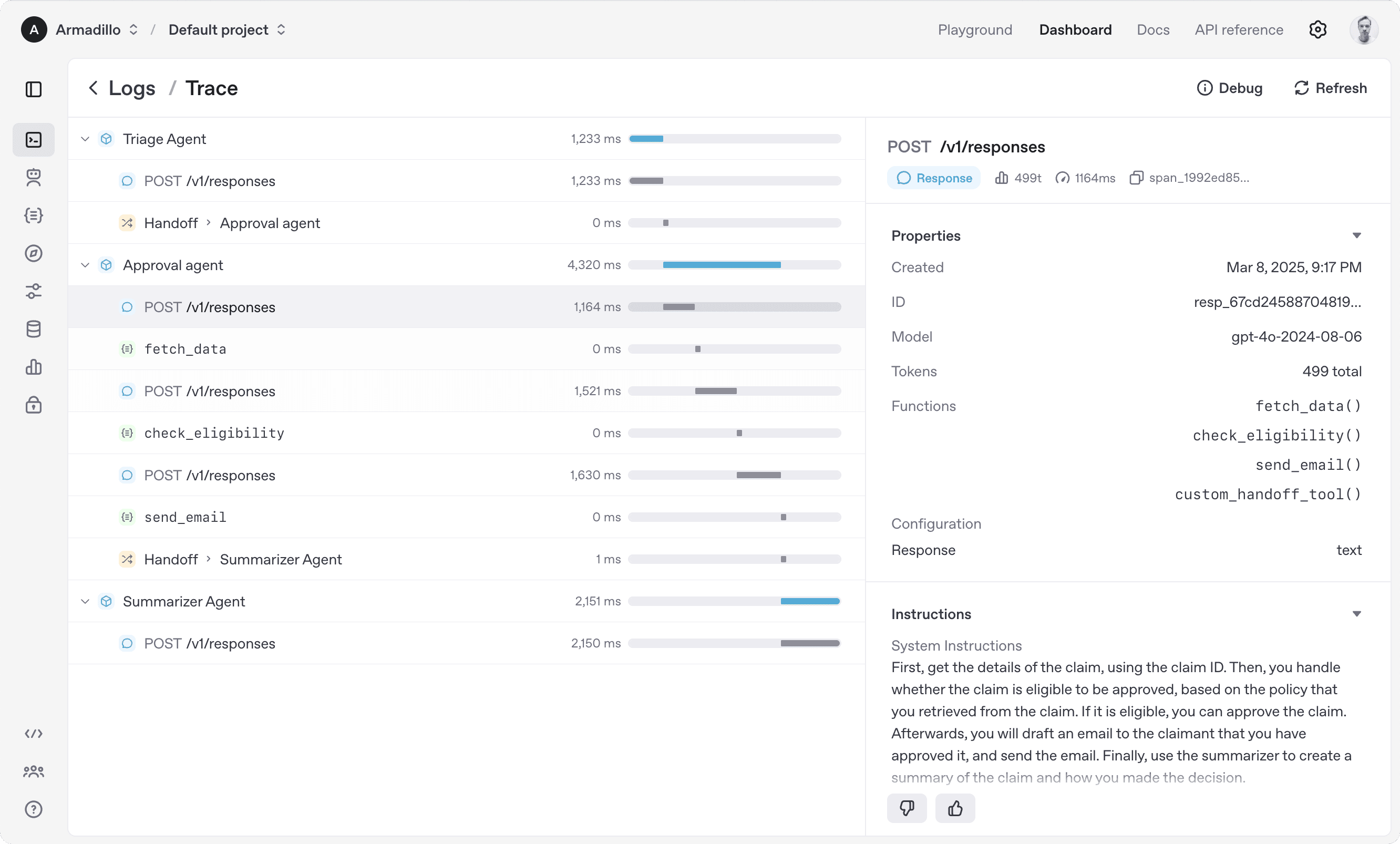
The OpenAI Agents SDK focuses on removing orchestration overhead while covering the essentials required for production agent systems. Its feature set clusters naturally into four areas.
1. Agent Primitives and Orchestration
At its core, the SDK exposes a small set of primitives that handle most agent workflows without additional abstractions.
Agents: Instruction-driven entities with access to tools and models.
Tools (Functions): Any Python or TypeScript function can be exposed as a tool with automatic schema generation and validation.
Handoffs: Native support for delegating tasks between agents without manually wiring state or control flow.
Guardrails: Input and output validation to constrain agent behavior and reduce unsafe or malformed responses.
This minimalist design avoids the cognitive overhead of graphs or state machines, making it easy to reason about execution paths early in development.
2. State and Memory Handling
The SDK manages conversational state within a session by default.
Built-in session history works out of the box
Optional persistence backends such as SQLite are supported
No native long-term or semantic memory is included
This is a deliberate tradeoff. The SDK handles short-term context cleanly but expects durable memory, retrieval, or personalization layers to be added externally as projects mature.
3. Observability and Tracing
Observability is one of the SDK’s strongest differentiators.
Automatic tracing of agent runs without custom instrumentation
Custom spans for deeper visibility into tool calls or logic branches
External integrations with tracing and workflow platforms
Most agent frameworks treat observability as an afterthought. Here, it’s built in from the start, reducing debugging time and production risk.
4. Model and Provider Support
While optimized for OpenAI models, the SDK is not limited to them.
Works with 100+ LLMs via the Chat Completions API
Optimized latency and token handling when using GPT-4o-class models
Provider-agnostic design reduces long-term lock-in
You get the best performance with OpenAI models, but the architecture does not force exclusivity.
What’s Missing by Design
The SDK intentionally avoids certain capabilities that other frameworks bundle in:
No graph-based workflow engine
No built-in vector memory or retrieval layer
No opinionated agent planning system
This keeps the surface area small but shifts responsibility to the developer when advanced behaviors are required.
Language Support: Python and TypeScript
The dual-language approach sets the OpenAI Agents SDK apart from Python-only alternatives. Both the Python and TypeScript/JavaScript versions support equal features for building multi-agent workflows.
The TypeScript implementation includes function tools that convert TypeScript functions into agent tools with automatic schema generation. Zod-powered validation provides type safety throughout the agent execution pipeline. Built-in tracing features match the Python version's observability features.
This cross-language support allows broader adoption across development teams. Backend Python developers and frontend JavaScript/TypeScript teams can use the same conceptual framework while working in their preferred languages. The npm package makes integration straightforward for Node.js applications.
The consistency between language implementations reduces context switching for teams working across different parts of the stack. Whether you're building server-side agents in Python or client-side interactions in TypeScript, the same patterns and concepts apply.
LangGraph Comparison
LangGraph offers deep customization through graph structures and excels at cyclical workflows, but learning its ins and outs can take time. Developers consistently report that LangGraph requires major upfront investment in learning graph concepts and state management even for simple agents.
In addition, the technical documentation, while detailed, isn't beginner-friendly. This complexity can slow down development cycles and increase onboarding time for new team members.
LangGraph's graph-based methodology provides granular control over agent workflows. You can define complex decision trees, loops, and conditional logic that would be difficult to implement in simpler frameworks. However, this flexibility comes at the cost of development speed and ease of use.
The architectural philosophy differs fundamentally from OpenAI's simplified approach. While LangGraph treats agents as nodes in a computational graph, the OpenAI SDK focuses on straightforward delegation patterns that most developers can grasp immediately.
When to Choose the OpenAI Agents SDK
The OpenAI Agents SDK focuses on production readiness with features like guardrails and standardized patterns for agent-to-agent handoffs. The lightweight architecture makes it accessible to developers familiar with OpenAI's API ecosystem.
Developers consistently report that the OpenAI Agents SDK requires just a few lines of code to get started. The well-written, easy-to-understand documentation makes building a pleasure.
Choose Agents SDK when development speed, simplicity, and OpenAI model integration are priorities. Organizations seeking rapid prototyping or teams already familiar with OpenAI's ecosystem will find the SDK particularly advantageous.
It excels for teams that want to focus on business logic rather than agent orchestration complexity. If your use case involves straightforward agent coordination without complex graph-based workflows, the SDK provides the right level of abstraction.
Teams working with GPT-4.1 Mini or other OpenAI models benefit from the tight integration and optimized performance characteristics built into the SDK.
Adding Memory with Mem0

As projects scale, memory in agents becomes essential. While the OpenAI Agents SDK offers short-term session history, it doesn’t provide durable or semantic memory out of the box. For applications that need context across sessions, personalized interactions, or continuous learning, external solutions are required.
Mem0 fills this gap by providing a universal memory layer for LLM applications. It turns stateless agents into adaptive systems that remember preferences, improve over time, and deliver more intelligent, personalized interactions.
In Mem0 performance benchmarks, latency was significantly reduced compared with custom memory setups, thanks to efficient compression of chat history. Success stories like OpenNote's scaling success highlight how the right memory architecture can cut costs while boosting reliability.
Integrated with the Agents SDK, Mem0 gives developers a production-ready combination: OpenAI’s simple orchestration plus persistent memory that makes agents truly intelligent. Check out the Mem0 OpenAI SDK integration tutorial for a deep look into how to integrate Mem0 with the OpenAI SDK.
FAQ
How do I get started with the OpenAI Agents SDK?
You can begin with just a few lines of code using either the Python or TypeScript/JavaScript versions. The SDK requires minimal setup and works with your existing OpenAI API integration.
What's the main difference between the OpenAI Agents SDK and LangGraph?
OpenAI Agents SDK focuses on simplicity, while LangGraph offers deep customization through complex graph structures that require understanding nodes, edges, and state management before building your first agent.
When should I add memory features to my agents?
Consider adding memory when your agents need to maintain context across sessions, personalize responses based on user history, or continuously improve performance over time.
Can I use the OpenAI Agents SDK with models other than OpenAI's?
Yes, the SDK works with 100+ other LLMs through the Chat Completions API despite being optimized for OpenAI models, preventing vendor lock-in while maintaining the framework's simplicity and rapid development features.
Final Thoughts on Choosing the Right AI Agent Framework
The OpenAI Agents SDK strikes a practical balance between ease of use and flexibility, making it a solid choice for developers who want production-ready agents without the overhead of more complex frameworks. Its design works well for teams focused on shipping quickly while still leaving room for customization as projects grow.
That said, no framework covers every requirement out of the box. Features like long-term memory and persistence often need to be layered on separately, depending on the use case. Tools such as Mem0 can complement the SDK in this area, but the core decision should come down to how much orchestration complexity your team is prepared to manage.
Subscribe To New Posts
Subscribe for fresh articles and updates. It’s quick, easy, and free.














