Smolagents vs Other AI Agent Frameworks: What's New in December 2025
Smolagents has quickly become one of the most talked about agent frameworks because of its minimalist, code-first design. In just about 1,000 lines of code, it enables developers to build powerful agents without the heavy abstractions that come with larger frameworks. September 2025 marked a turning point with new vision support and significant industry investment driving more attention to its approach. This post explains how smolagents works, how it compares to alternatives like AutoGen and LangGraph, and how you can optionally extend it with a persistent memory layer if your project requires stateful context.
TLDR:
Smolagents uses code execution instead of tool calling, reducing steps by approximately 30%. Its entire framework is only about 1,000 lines of code.
September 2025 saw vision support added to smolagents, as well as $100M of industry investment in agents.
Smolagents emphasizes simplicity, AutoGen emphasizes multi-agent chat, and LangGraph supports complex workflows.
What Is Smolagents?
Smolagents is a library that lets you run powerful agents in a few lines of code. Simplicity is its core value proposition: The logic for agents fits in approximately 1,000 lines of code, making it one of the most minimalist AI agent frameworks currently available.
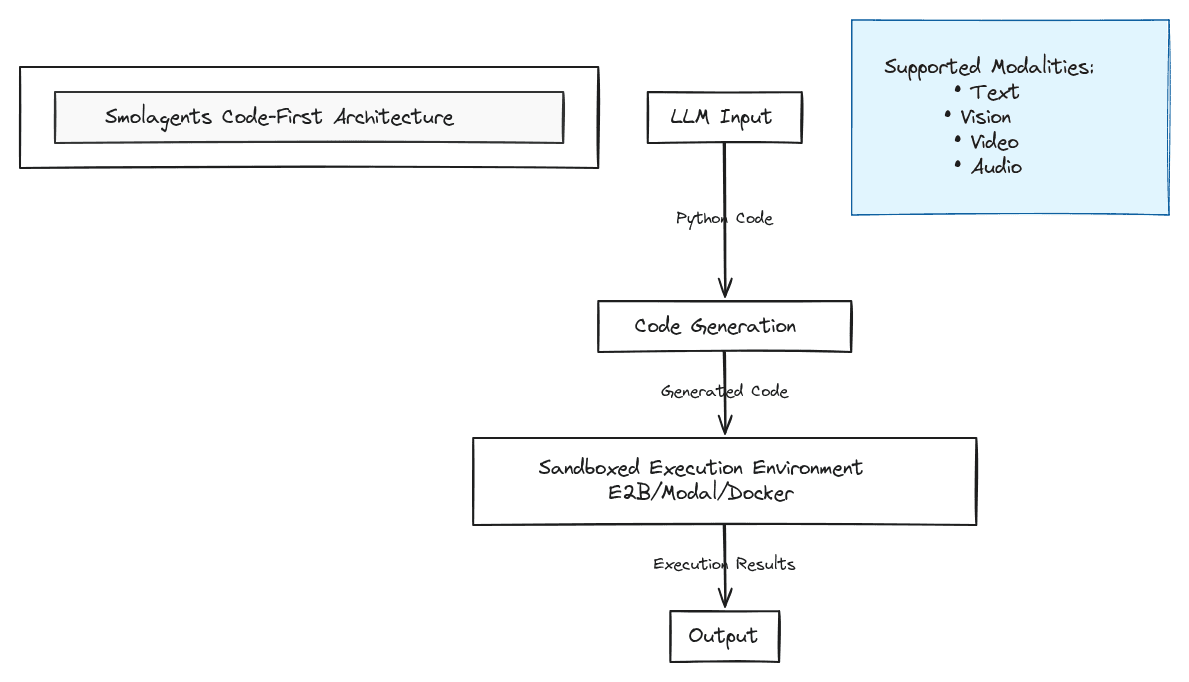
The framework gained major attention in early 2025 with its unique approach to agent architecture. Unlike traditional frameworks that rely on JSON or text-based tool calling, smolagents implements first-class support for Code Agents. These agents express their actions directly as executable Python code, rather than treating code generation as an afterthought.
To handle security concerns with code execution, smolagents supports running in sandboxed environments via E2B, Modal, Docker, or Pyodide with Deno WebAssembly. This architectural choice sets it apart from traditional tool-calling frameworks and provides a more direct path from intent to execution.
The framework's model-agnostic design supports any LLM, whether it's a local transformers model, an Ollama deployment, a Hub-hosted model, or a commercial API from OpenAI and Anthropic via LiteLLM. It's also modality-agnostic, supporting text, vision, video, and even audio inputs, depending on model support.
Smolagents represents a shift toward code-first agent design, where the composability and generality of code reduce execution steps by approximately 30%, compared with traditional tool-calling methods.
How Smolagents Works
Smolagents operates differently from conversation-based agents by focusing on executable code as the primary action mechanism. The framework uses an extensive 200-line system prompt for its Code Agent. This is a highly structured and controlled approach to autonomy within bounded task domains.
The level of autonomy is high within the supplied tools and rules, but the framework maintains control through its code-centric approach. Instead of generating abstract action descriptions, agents write Python code that directly accomplishes tasks, using the inherent composability of programming languages.

The framework's architecture supports multiple models through its flexible integration layer. Whether you're using local models for privacy or cloud-based solutions for scale, smolagents adapts to your infrastructure choices without requiring major code changes.
Comparing Smolagents With Other Frameworks: LangChain, AutoGen, CrewAI
The table below provides a high-level comparison between Smolagents and other frameworks.
Feature | Smolagents | LangChain | AutoGen | CrewAI |
Primary design goal | Minimal, model-native agent loops | General-purpose LLM app framework | Multi-agent conversation & coordination | Role-based multi-agent task execution |
Abstraction level | Very low (plain Python) | Medium–high (chains, LCEL) | Medium (agent/message abstractions) | Medium (roles, tasks, flows) |
Multi-agent support | No | Limited / add-on | First-class | First-class |
Tool calling & execution | Direct Python functions | Extensive tool ecosystem | Tool-aware agents | Task-scoped tools |
Memory & persistence | None built-in | Optional / pluggable | Basic conversational | Task-level memory |
Control flow & orchestration | Manual | Graphs, routers, retries | Conversation-driven | Sequential / hierarchical |
Production readiness | Prototype / embedded use | Strong ecosystem | Emerging | Emerging |
Ideal use cases | Ephemeral agents, research, glue code | RAG, agents, enterprise apps | Collaborative agents, simulations | Structured team workflows |
In summary:
Smolagents are best viewed as agentic building blocks, not a platform.
LangChain is the most flexible for production systems but has higher complexity.
AutoGen excels when agents need to talk to each other.
CrewAI shines in role-based, goal-oriented task execution with clear delegation.
Performance and Scalability Considerations
In terms of framework performance, different approaches show distinct advantages. Smolagents caters to developers focused on running smaller models or HuggingFace-hosted setups, highlighting performance and openness, though its onboarding flow remains rough.
One of the biggest challenges in agent development is striking the right balance between giving the AI enough autonomy to handle tasks dynamically and maintaining enough structure for reliability. Each framework has its own philosophy, from explicit graph-based workflows to lightweight code-driven agents.
AutoGen and smolagents fall into the high-autonomy camp, while frameworks like LangGraph lean more toward control. The scalability challenges vary by use case:
Code execution overhead: Smolagents must manage sandboxed environments for each code execution.
Memory management: Most frameworks lack persistent memory, requiring external solutions.
Error handling: Code-first approaches need strong retry mechanisms for failed executions.
Resource allocation: Multi-agent frameworks require careful resource management to prevent conflicts.
A production-grade framework must allow agents to maintain context throughout tasks, support retries, and provide detailed logs and traces.
Use Cases and Best Fit Scenarios
Different frameworks excel in specific scenarios based on project complexity and requirements. You need to assess whether you're building a simple chatbot or a complex multi-agent system before choosing your framework. Here are some general recommendations for using smolagents:
Single-agent, short-horizon reasoning. For example, if the task can be completed in seconds to minutes, does not require long-term memory, or has limited branching or retries. Some examples are data transformation or analysis, code refactoring, and one-shot planning or decomposition.
Tool-heavy workflows with simple logic. Smolagents are perfect for this use case when the model decides which tool to call, the developer wants explicit control over tool execution, and tools are local Python functions or APIs. Some examples include file parsing/summarization, API aggregation, and simple RAG pipelines.
Prototyping and research. Smolagents are ideal for this when you're exploring agent behavior, tuning prompts, tools or reasoning styles, or you want minimal ceremony and fast iteration. Some examples are benchmark experiments and early-stage product exploration.
Why Memory Matters in AI Agents
Frameworks like smolagents, AutoGen, and CrewAI are effective at coordinating agent behavior but generally lack persistent memory. Without it, agents reset each session, even with large context windows.
Mem0 provides this missing layer by persisting interactions across sessions. Benchmarks show a 26% performance improvement over OpenAI baselines across single-hop, temporal, multi-hop, and open-domain tasks, while reducing computational overhead.
Mem0 integrates with smolagents, LangGraph, AutoGen, and other frameworks in Python or JavaScript, making it straightforward to add statefulness without altering core logic. This allows agents to retain context, recall past interactions, and deliver more consistent, personalized results. Check out the Mem0 integration docs for details on how to connect Mem0 to frameworks.
FAQ
What's the main difference between smolagents and LangChain for building AI agents?
Smolagents focuses on code-first execution where agents write Python code directly to accomplish tasks, while LangChain uses higher-level abstractions and tool-calling mechanisms. Smolagents offers simplicity and transparency, whereas LangChain provides complete tooling for complex workflows but with a steeper learning curve.
When should I choose smolagents over a multi-agent framework like AutoGen or CrewAI?
Choose smolagents when you need simple, individual agents that solve problems through direct code execution, want minimal abstractions, or are building rapid prototypes. Use AutoGen for conversational multi-agent systems or CrewAI when you need role-based team collaboration between specialized agents.
How does Mem0 integrate with smolagents and other frameworks?
Mem0 exposes a language-agnostic memory layer that can plug into any agent framework. With smolagents, developers can wrap the code agent’s execution loop with Mem0’s APIs so that intermediate outputs, user inputs, and state transitions are persisted between runs. For frameworks like LangGraph or AutoGen, Mem0 can be attached at the node or message-passing layer to provide long-term recall across graph states or conversational turns. This lets teams preserve relevant context across sessions without modifying the core framework logic.
What are the security considerations when using smolagents' code execution approach?
Smolagents handles security through sandboxed environments including E2B, Modal, Docker, or Pyodide with Deno WebAssembly. This prevents malicious code execution while maintaining the framework's core advantage of direct Python code generation and execution.
Final Thoughts on Choosing the Right AI Agent Framework
Different frameworks address different needs: smolagents emphasizes minimal code-first execution, AutoGen supports conversational multi-agent workflows, and LangGraph enables complex graph-based orchestration. A common limitation across all of them is the absence of persistent memory, which resets context at the end of each session. Integrating a memory layer such as Mem0 allows agents to retain information across interactions, improving reliability and personalization without changing the underlying framework.
Subscribe To New Posts
Subscribe for fresh articles and updates. It’s quick, easy, and free.














